Advertising is a form of marketing communication used to promote or sell something, usually a business's product or service. In year 10 Media we look at the different Advertising mediums around and investigate what career opportunities there are within this field.
The assessment piece for this unit is, ‘The Pitch’. You will be required put together an Advertising Campaign on a product or service of your choice. For more information download the booklet to the right.
Code & Conventions of ADVERTISING
Codes and conventions are important in advertising for the creation of meaning. For an advertisement to be successful it is important that the target audience responds to it in the way that the producer intended. A successful advertisement will contain codes and conventions that the audience is familiar with. For the target audience to connect with an advertisement they need be feel that they can trust, interact and bond with it and this is assisted by the conventions and codes within it.
Symbolic Codes
Mise En Scene, props, settings, costumes and colors. These codes help symbolize the meaning of something, for example if you see a very well dressed man in an elite sports car in an exotic location the audience would automatically think that he is successful and link the product with success.
Written Codes
Headlines, captions, speech bubbles, language style
Technical Codes
Camera techniques, framing, depth of field, lighting, exposure, sound and editing.
These codes include camera angles, shots, lighting, editing and sound. Camera, position, angles and shots are can be used to show different perspectives. The lighting can be used to create an atmosphere and/or mood. Sound can be used for dialogue, as a voice over to speak about the product is or music also to create a mood.
ADVERTISING – THE PITCH – CHECK LIST
Slide 1: Your advertising company’s name (think of your branding and have a consistent colour, font scheme throughout your Pitch)
Slide 2: Your product or service (name and give a visual to your product/service)
Slide 3: Methods of appeal. List at least three methods of appeal that you will be using. (make sure you include some examples here. It doesn’t have to be your product or service it can be another ad that uses the same methods of appeal in their campaign)
Slide 4: Audience. Detail and explain your audience. Also give visual. (make sure you break them down using Demographics / Psychographics & Geographics)
Slide 5: Code and Conventions of Advertising and Story-Telling. (Symbolic, Written & Technical). Reveal which ones you will focus on and why.
Slide 6: Advertising Mediums. List which Advertising mediums you plan to create. For example: A social media campaign or A television commercial or a Radio commercial etc.
Slide 7: Media Buying – List where you plan to advertise. For example, what show you plan to tread your TV Advertisement through. Or which Influencer you plan to product place your product or service in. Which radio segment or location of Billboard etc. Or detail which magazine and how big the layout will be and where it will be. Most importantly Why?
Slide 8: Advertising Rate Card – Here you will provide an image of what your advertising rate will look like according to what Media you are buying.
Slide 9: Product Placement: Detail when and where you plan to launch your campaign. What month and location. For example; in The City just before Christmas. And why? Or you might planning to promote your product on an actual Film or TV Series.
Slide 10: Marketing & Evaluation: From the booklet and website you will see a list of Marketing & Evaluation ideas. Select TWO and explain why?
Slide 11: Brand Association: Brand identity is crucial to your product or service. This makes a huge impact on the way your audience can identify with your product or service. (Budget, Luxury, Quality). Explain which and why.
Slide 12: Budget – Draw a table and map out your costs. Detail all your expenses and add them up and reveal the cost of the campaign.
Slide 13: This is where you put your actual ADVERTISEMENT.


AUDIENCE BREAKDOWN
Demographic: Gender, Age, Income, Family.
Geographic: Where you live, How you live, Where you holiday, Where you hang out, Where you buy things – online/in-store.
Psychographic: Your likes, Dislikes, Hobbies, Your thoughts on things, Social media use, Who you hang out with, Buying trends, Do you follow others, Are you a leader, Introverted, Extroverted, How important social media is to you, Behaviours, Positive or negative mindset, Out Spoken, Political, Activist etc.
BRAND ASSOCIATION
Brand identity is crucial to your product or service. This makes a huge impact on the way your audience can identify with your product or service.
Brands identity often falls into three areas:
LUXURY: A costly brand and customers expect a certain level of luxury and eliteness. Customers expect to pay more for your product or service.
QUALITY: Your costumers expect to pay for the quality. The want the product or service to last and be durable.
BUDGET: Customers don't have high expectations other than to pay less for your product or service.
The role of the Media Buyer
As a media buyer you will negotiate, purchase and monitor advertising space and airtime on behalf of clients. The aim is to reach the highest number of people in the target audience at the lowest possible cost. Roles tend to be based in advertising and media agencies.

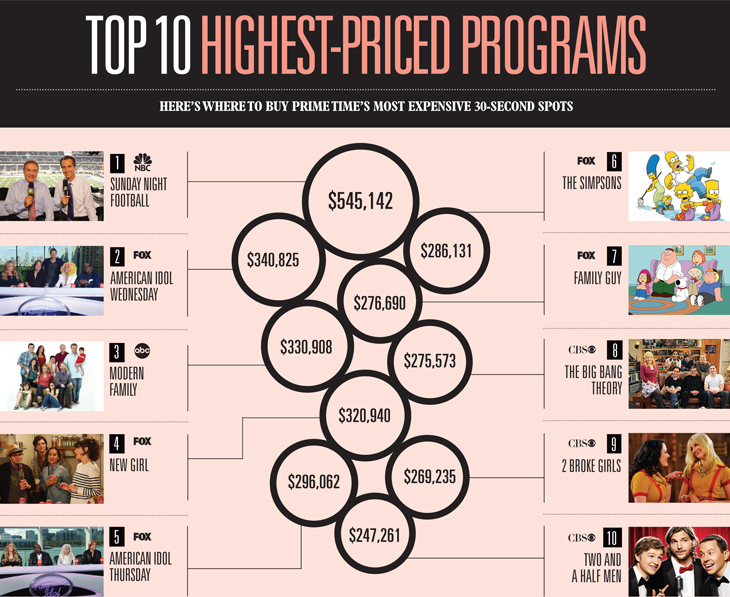
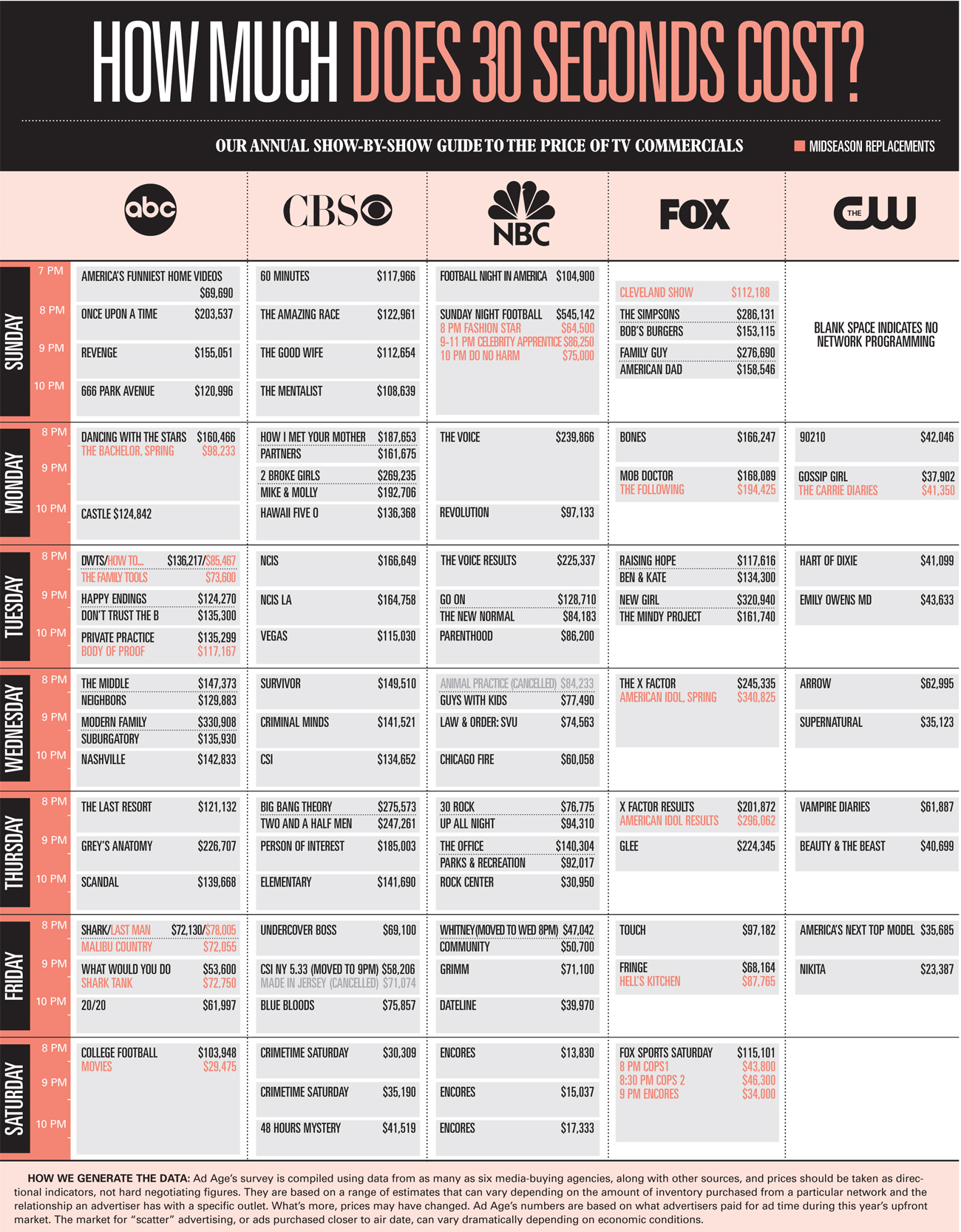
ADVERTISING RATE CARDS
A rate card is a document provided by a television network, social media platform, billboard, newspaper or other print publication featuring the organisation's rate for advertising. It may also detail any deadlines, demographics, policies, additional fees, and artwork requirements.
Television Advertising Rate Card
Youtube Advertising Rate Card

Magazine Advertising Rate Card
Print Publication Rate Card

Billboard Rate Card

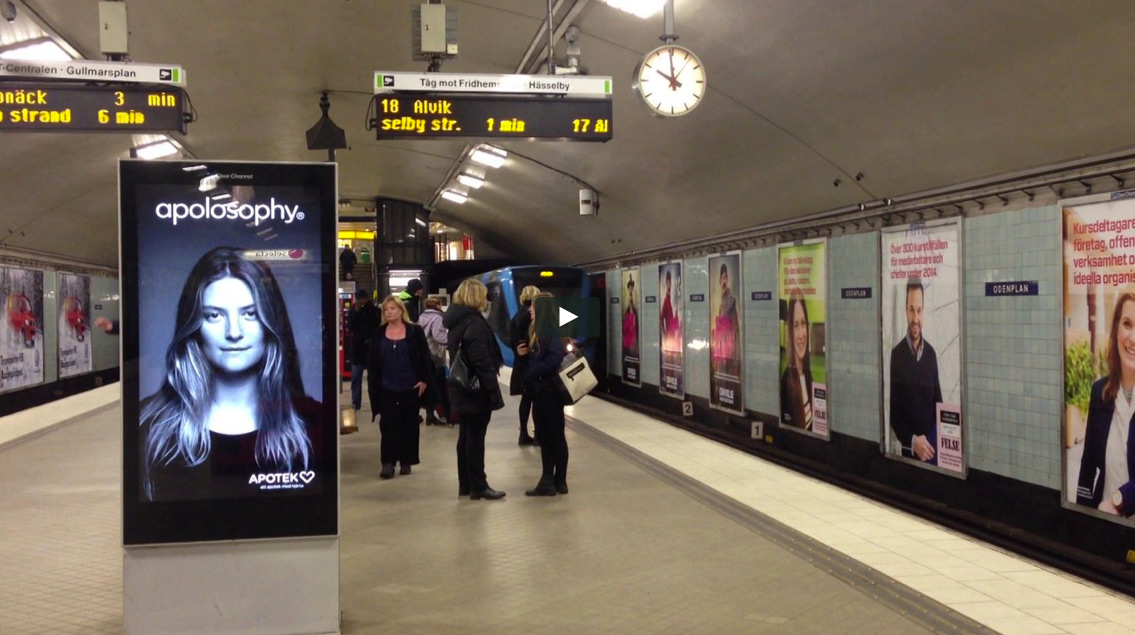
Train Station Advertising
Train station advertising opportunities exist across many stations throughout Melbourne, Sydney, Perth and Queensland.
Due to the incredibly high dwell time, rail advertising delivers high engagement, and high impact advertising to a more receptive a captive commuter audience. From complete station domination, through to the rail platform advertising, train internals and train externals, whether is it static or digital billboard advertising rail offers excellent advertising Return on Investment.
On average, rail travelers spend 12 minutes waiting on the platform per trip. Cross Track panels enable advertisers to engage with a much more captive audience. 94% of train commuters have high or some exposure to advertising in railway stations.
Subway Advertising

Marketing / Research / Evaluation
Researchers often use more than one research design. They may start with secondary research to get background information, then
conduct a focus group (qualitative research design) to explore the issues. Finally they might do a full nation-‐wide survey (quantitative
research design) in order to devise specific recommendations for the client.
Types of marketing research: Marketing research techniques come in many forms, including:
Ad Tracking – tracking a brand’s performance using measures such as brand awareness, brand preference, and product usage.
Advertising Research – used to predict effectiveness of advertisements measured by the ad’s ability to get attention to build the
brand’s image, and motivate the consumer to purchase the product or service.
Brand equity research -‐ how favorably do consumers view the brand?
Brand association research -‐ what do consumers associate with the brand?
Brand attribute research -‐ what are the key traits that describe the brand promise?
Brand name testing -‐ what do consumers feel about the names of the products?
Concept testing -‐ to test the acceptance of a concept by target consumers.
Coolhunting -‐ to make observations and predictions in changes of new or existing cultural trends in areas such as fashion, music,
films, television, youth culture and lifestyle.
Buyer decision processes research -‐ to determine what motivates people to buy and what decision-‐making process they use.
Price elasticity testing -‐ to determine how sensitive customers are to price changes.
Fast Food Ad Verses Reality
15 Tricks used in Advertising
Perfume print advertisement by students using the light box

TV Advertisement - Watch
THE PITCH
For this task we are creating an Advertising Pitch. Here is an example of a Powerpoint presentation alongside their TV ad for their product.